|
AP.GUI
AP.GUI es una biblioteca para escribir programas
con interfaz gráfica usando Haskell.
Su diseño es similar a otras bibliotecas diseñadas para el mismo fin como son
[wxHaskell]
y
[HToolkit]
.
Ejemplo 1
------------------------------------------------------
-- Simple buttons demo
--
-- Pepe Gallardo, 2004
------------------------------------------------------
import AP.GUI
main :: IO ()
main = gui prog
prog :: IO ()
prog = do { w <- window [ title =: "window"
, on windowClose =: quit
]
; b1 <- button [ text =: "Button"
, bgColor =: blue
, color =: white
, on action =: putStr "Pressed!\n"
] w
; im <- loadImageFrom "../images/rose.gif"
; b2 <- button [ photo =: im
, bgColor =: white
, on action =: putStr "Rose pressed!\n"
] w
; b3 <- button [ text =: "Disabled"
, enabled =: False
, relief =: Groove
] w
; b4 <- button [ text =: "Quit"
, font =: bold (arial 14)
, on action =: quit
] w
; w!:layout =: b1 <.< b2 <.< b3 <.< b4
}

Ejemplo 2
------------------------------------------------------
-- RadioButton demo
--
-- Pepe Gallardo, 2004
------------------------------------------------------
import AP.GUI
import Monad
main :: IO ()
main = gui prog
where
prog = do { w <- window [ title =: "RadioButton demo"
, on windowClose =: quit
]
; l <- label [] w
; let mkRB txt =
do { im <- loadImageFrom ("images/a"++txt++".gif")
; rb <- radioButton [ text =: txt
, on action =: do { l!:photo =: im }
] w
; return (rb,im)
}
; (rbs,ims) <- mapAndUnzipM mkRB ["Dog", "Cat", "Bird"]
; rg <- radioGroup [ radioButtons =: rbs ]
; let initSel = 0
; l !: photo =: ims !! initSel
; (rbs!!initSel) !: checked =: True
; f <- frame [ layout =: vertical rbs
, relief =: Groove
] w
; q <- button [ text =: "Quit"
, on action =: quit
] w
; w!:layout =: pad 10 f <.< pad 10 l ^.^ q
}

Ejemplo 3
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-- Draws sierpinski Triangle (taken from HSOE)
--
-- Pepe Gallardo, 2004
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
import AP.GUI
minSize :: Int
minSize = 8
main :: IO ()
main = gui prog
where
prog = do { w <- window [ title =: "Sierpinski"
, on windowClose =: quit
]
; c <- canvas [ size =: sz 400 400, bgColor =: white ] w
; q <- button [ text =: "Quit", on action =: quit, enabled =: False ] w
; w!:layout =: c ^.^ q
; sierpinski c 50 300 256
; q!:enabled =: True
}
sierpinski :: Canvas -> Int -> Int -> Int -> IO ()
sierpinski c x y size
= if size <= minSize
then do fillTri c x y size
else do { let size2 = size `div` 2
; sierpinski c x y size2
; sierpinski c x (y-size2) size2
; sierpinski c (x+size2) y size2
}
fillTri :: Canvas -> Int -> Int -> Int -> IO ()
fillTri c x y size =
do { polygon [ pt x y, pt (x+size) y, pt x (y-size), pt x y ] [ fillColor =: blue ] c
; update
}

Ejercicios
-
Escribe un programa con la siguiente interfaz para
calcular el factorial de un número. Al pulsar el botón "calculate!"
debe mostrarse en la segunda línea el factorial del número
introducido en la primera. Usa los controles Entry, Label y
Button .
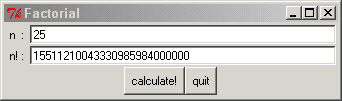
-
Escribe algún programa de tamaño medio (elígelo tu) usando la librería AP.GUI.
A la hora de corregir la práctica, el profesor
valorará, además de la complejidad del programa, su correcto funcionamiento, junto con la calidad y claridad del código. Especialmente
se valorará la descomposicón del programa en funciones de modo adecuado, la reutilización de código y el uso de características
de Haskell como las funciones de orden superior, las listas por compresión, etc.
|